-
Inlays & Onlays
Inlays & Onlays
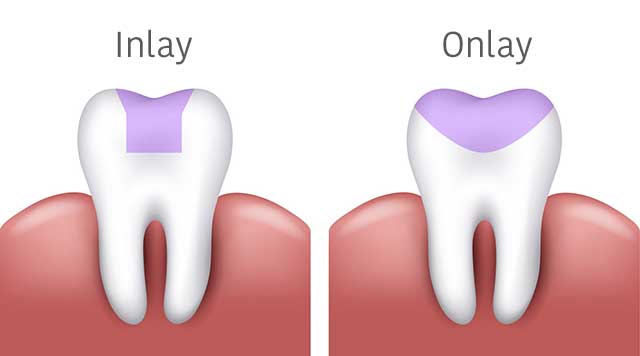
Inlays
It is a treatment chosen by the practitioner when the restorations made directly in the mouth (ex: composites and amalgams) do not achieve a good result (ex: lack of suitable contact with the neighboring tooth). The piece, metal, ceramic or resin, is cast or machined in the laboratory and then attached to the tooth using a bonding composite.
Onlays
It is a partial prosthesis made when the tooth destroyed by decay or a fracture has:
- Significant decay, which contraindicates restorations made directly in the mouth by the dentist, such as composites and amalgams, which may present the risk of fracturing because they are not strong enough
- Few residual tooth walls.
After the preparation and the impression, the onlays will be made in the laboratory, they can be made of metal, resin, or ceramic, their fixation on the tooth is done with the bonding composite.
-
Endodontics & Devitalization
Endodontics & Devitalization
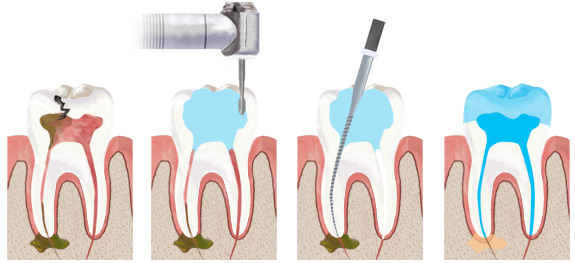
Endodontics is the treatment of the inside of the tooth (devitalization). The dentist must perform endodontics in order to clean and disinfect the internal part of the tooth and then close it. When the cavity reaches the pulp (the nerve), the patient begins to feel cold, hot or chewing pain (see diagram on the left). When the tooth is left untreated, the decay infects the bone, and the patient may feel radiating pain or may even swell (see diagram on right).
Endodontic treatment consists of:
- Eliminate what remains of the infected or potentially infected nerve inside the tooth (dental pulp)
- Thoroughly clean the inside of this tooth, by a mechanical action: scraping the inner surface of the root using manual or motor-mounted endodontic files. This cleaning is facilitated by disinfectants
- Achieve root closure.
For this, the dentist generally performs a local anesthesia, so that the gesture is not painful. An adequate opening is made on the tooth, to access the pulp (nerve).
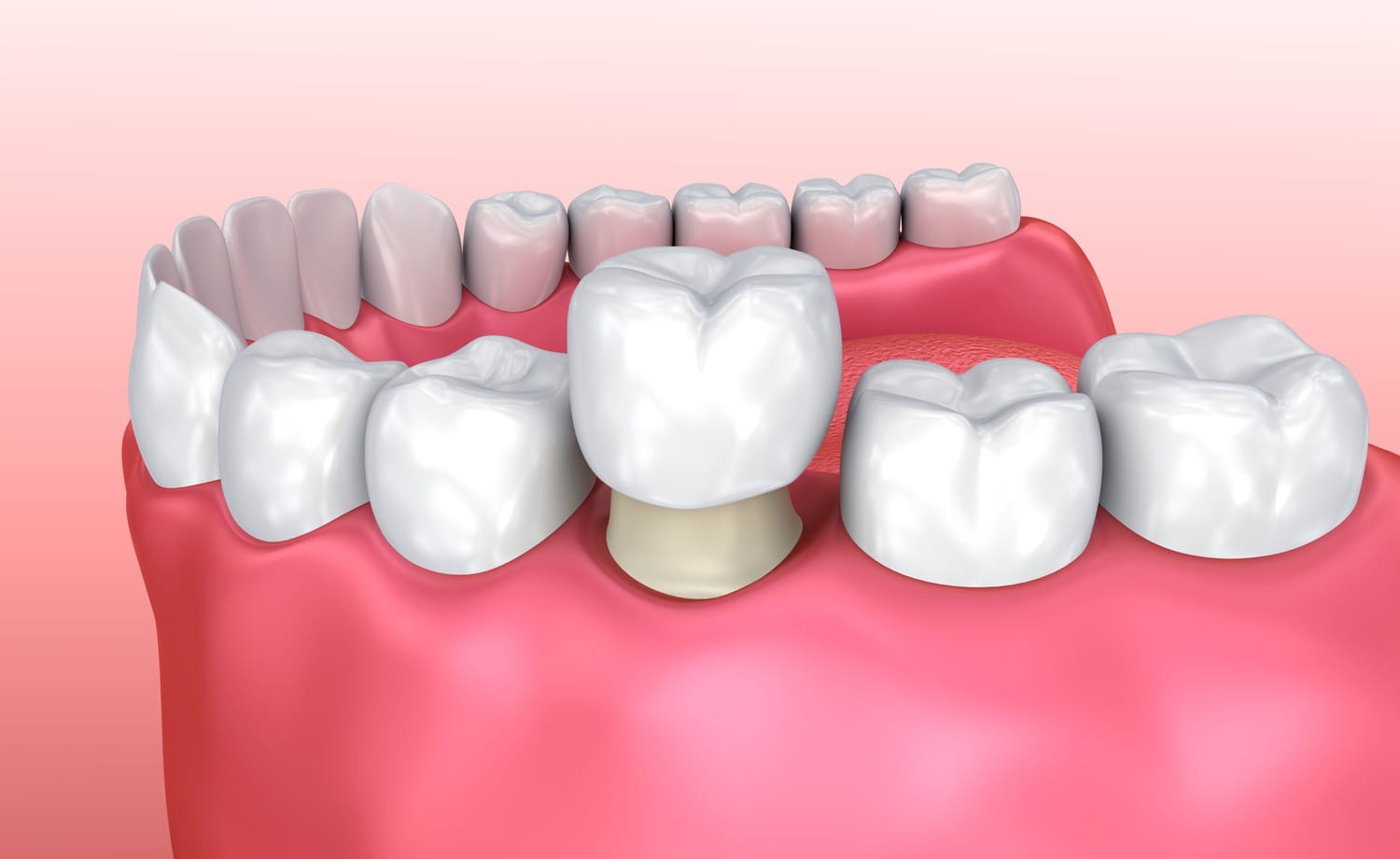
After the roots have closed, the tooth will have to be reconstructed, either with a composite (materials that have the color of the tooth) if this tooth is not too dilapidated, or with a prosthetic reconstruction (crown or onlay) if it is too dilapidated, in order to protect the tooth from a probable fracture, and to ensure the function of the tooth.
Technologies: mechanized endodontics
Endodontic treatment can be performed by modern nickel titanium instruments. They are very flexible and are activated by an electric motor. A detector makes it possible to locate the end of the root without traumatizing the bone. This is called mechanized endodontics. This technology makes it possible to perform endodontic treatment (devitalization) more quickly and precisely, and very often in a single appointment.
-
Dental hygiene tips
Dental hygiene tips
What toothbrush?
The manual toothbrush used must have soft bristles, with a small head to reach all corners. Too hard bristles can wear down your enamel and attack your gums significantly in the long term. Better is a soft brushing and a little longer than an aggressive brushing which could damage your enamel and your gums.
The electric toothbrush: circular type with alternating quarter-turn rotary motion. It significantly improves oral hygiene in people who have difficulty performing manual brushing (motor or mental deficit).
What brushing and how often?
Attention! While brushing is essential, it can also do more harm than good if done incorrectly. At least 2 brushings per day morning and especially in the evening. Brushing movements are often done inappropriately. At the beginning of the movement, the bristles of the brush must be laid on the gum towards the tooth. Be careful to brush all surfaces of the teeth.
Is brushing between teeth necessary?
Interdental brushes and dental floss should be an integral part of brushing. Indeed, the toothbrush whether electric or manual does not clean between the teeth. A large part of dental problems (caries, loosening, etc.) start between the teeth since bacteria stagnate there. If the gums are in good health, brushing should be done once a day, ideally in the evening. In case of gum disease, it may be necessary to do this 2 to 3 times a day. If the interdental spaces are too narrow, the brushes should be replaced with dental floss.
Toothpastes, what to choose?
Toothpaste is a complement to brushing, its purpose is to bring fluoride to the teeth. The amount and concentration of fluoride must be adapted to age. Fluoride was an important factor in reducing cavities when it was introduced into toothpastes because it strengthens the enamel. The other functions (antiscale, whitening, antibacterial) are secondary. Beware of whitening toothpastes and toothpastes for smokers as they are abrasive and can damage tooth enamel.
Mouthwashes, when to use them?
Mouthwashes are antiseptics, they should not be used daily outside of the cures prescribed by the dentist to avoid bacterial resistance. Under no circumstances can mouthwash replace good brushing.
-
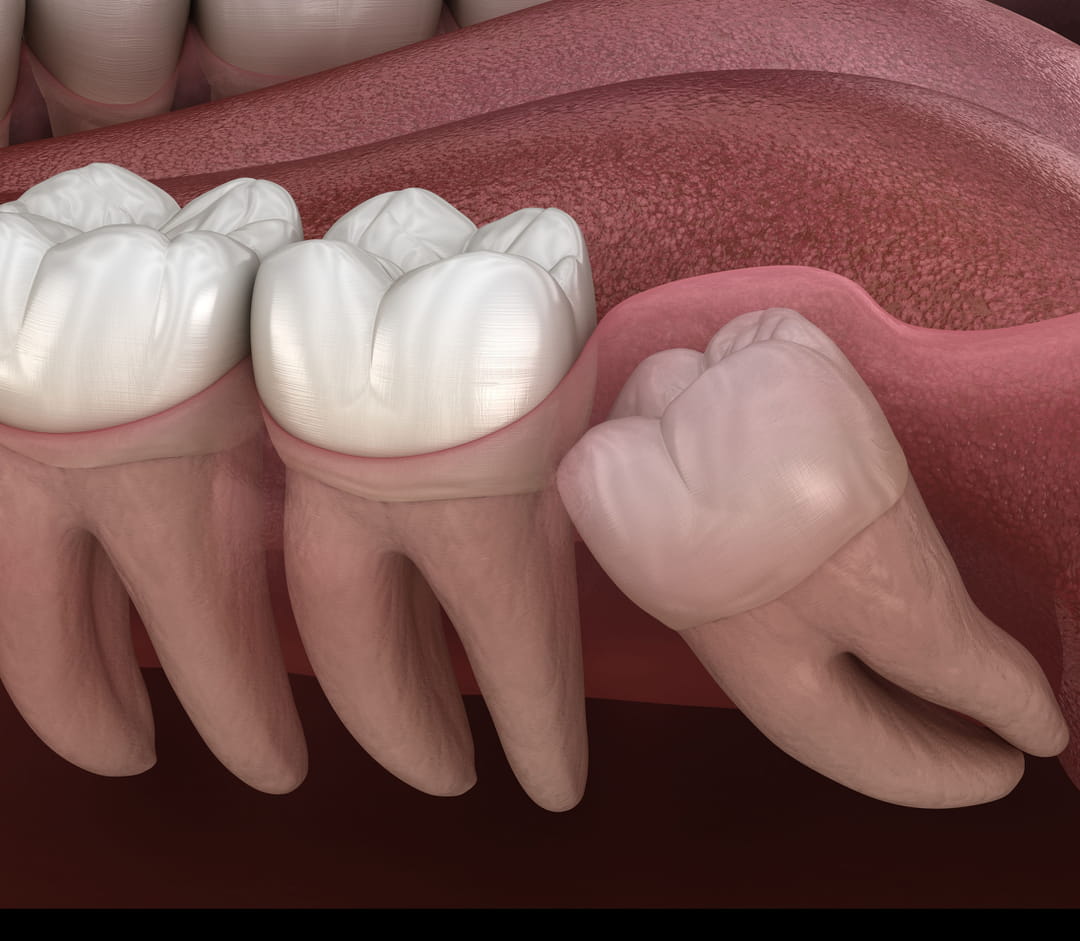
wisdom tooth extraction
wisdom tooth extraction
What are wisdom teeth?
Wisdom teeth, also called third molars, are the last teeth to develop. They have a wide variety of shape and size depending on the individual. They are positioned completely at the back of the dentition, behind the 2nd molars. . Wisdom teeth generally erupt in the mouth towards the end of adolescence; they generally appear in the mouth between the ages of 16 and 25 and root formation ends in the twenties.
The absence of wisdom teeth is becoming more and more frequent these days, new eating habits could be the cause.
Why remove them?
The total or partial extraction of wisdom teeth is the most common oral surgical procedure. It takes place under local anesthesia, and more rarely, under general anesthesia. There are many reasons for extracting wisdom teeth:
- For lack of space:
In the context of orthodontic treatment, when the teeth clearly do not have room on the arch. “Wisdom teeth are extracted before they are completely formed, we speak of germectomy (extraction of the tooth in the germ state). This intervention can be performed from the age of 12-14 years. This operation is prescribed after having carried out an X-ray of the two jaws called panoramic.
- Due to evolutionary accidents:
When the tooth does not erupt as it should, it can cause various problems: The most common is “pericoronitis”, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. This infection occurs on wisdom teeth that are halfway out, providing an entry point for bacteria. Pain, discomfort, difficulty opening the mouth (trismus), difficulty eating (dysphagia)… are generally present. Faced with such a problem, the dental surgeon will first control the infection by prescribing antibiotics and mouthwashes so that everything can then get back to normal quickly. But when the infection tends to repeat itself (two or three times), it is better to proceed with the extraction of wisdom teeth. Other possible incidents:
- In case of caries:
Due to their atypical morphology, the treatment of cavities occurring on wisdom teeth can be problematic. Faced with the greater risk of recurrence, the option of extraction can be retained.
- As a preventive measure:
However, opinions may differ when it comes to preventive extraction. Some will prefer to monitor an asymptomatic tooth instead of extracting it, especially if the x-ray indicates a proximity between it and the inferior alveolar nerve. Indeed, in the case where such proximity exists, caution is required not to cause damage to the nerve. Finally, in some people, the space available and the angulation of the tooth are optimal and allow a normal eruption. For these, it is of course useless to carry out the extraction.
How is the intervention carried out?
The procedure is not painful, in the vast majority of cases. X-rays are very helpful to your surgeon in planning surgery. Depending on the inclination of the tooth, its degree of impaction and its proximity to the inferior alveolar nerve, the procedure can be modified. The surgeon will opt for a simple extraction, if the tooth is present in the mouth, or a complex extraction if the tooth is impacted or semi-impacted. A complex extraction, also called a surgical extraction, involves the surgeon incising the gum, cutting the jaw bone to release the tooth, and closing the incision with stitches. Sometimes it may be necessary to cut the wisdom tooth into several pieces in order to be able to remove it. The surgeon will explain to you the various possible anesthesia options and will advise you taking into account the importance of your surgery, your state of health and your level of apprehension regarding the extraction. . .
What are the potential complications ?
As with any surgery, however well performed, there are risks associated with the extraction of wisdom teeth. Although the postoperative consequences are generally temporary
1. Bleeding: It is frequent and minimal for a few hours. If necessary, apply a sterile compress to the extraction area and bite on it for ten minutes. In order not to evacuate the blood clot which has formed in the alveolus, mouthwashes must be prohibited for the first two days.
2. Pain: It is more frequent below than above. It often yields with prescribed painkillers and disappears within a few days.
-
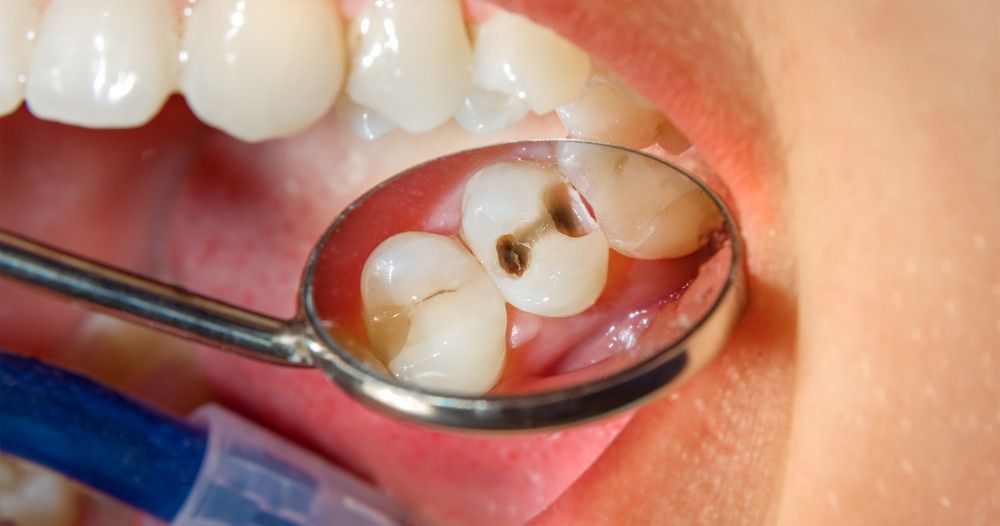
Thoot Decay Treatment
Tooth decay treatment
How can the appearance of cavities be prevented?
Perfect control of dental plaque through regular and effective cleaning as taught by the health professional, using the necessary hygiene means prescribed by the dentist and individualized for each case (toothbrush, dental floss brush etc .) ; A balanced diet, without unhealthy habits such as snacking; Regular monitoring, at least twice a year, of the teeth by the dentist is recommended.
What should we do if we are affected by this disease?
Only a dentist can treat a decayed tooth, once the disease has set in, it is irreversible and cannot be stopped by medication. The disappearance of the pain does not mean that the disease has been stopped.
What will happen if I do not treat a decayed tooth?
Caries is a disease that destroys the tooth. If the tooth is not treated, the destruction can reach the nerve of the tooth, then the root, then the bone. The greater the destruction, the less chance the tooth will have of being preserved in the mouth.
What will happen if the destruction reaches the nerve?
Once the nerve has been reached, the only way to preserve the tooth in the mouth is to do endodontic treatment, which is known as devitalization. (see also endodontics section)
What will happen if the destruction reaches the bone?
In general, the affected bone means that the dental destruction is quite advanced. In the majority of cases, the tooth cannot be saved and must be extracted. (See also the surgery section)
A decayed and cared tooth, can it be decayed again?
Yes, caries affects all dental tissues that are not cleaned. A composite, amalgam, or crown cannot protect the tooth from decay.